Introduction:
Mumps, a contagious viral infection, predominantly affects the salivary glands, leading to swelling and discomfort. Despite its rarity in countries with widespread vaccination, outbreaks still occur. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment of mumps is crucial for effective management and prevention.

Causes of Mumps:
Mumps is caused by the mumps virus, belonging to the Paramyxovirus family. It spreads through respiratory droplets from an infected person’s coughs or sneezes. The virus can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces. Lack of vaccination or incomplete vaccination increases susceptibility to mumps.
Symptoms of Mumps:
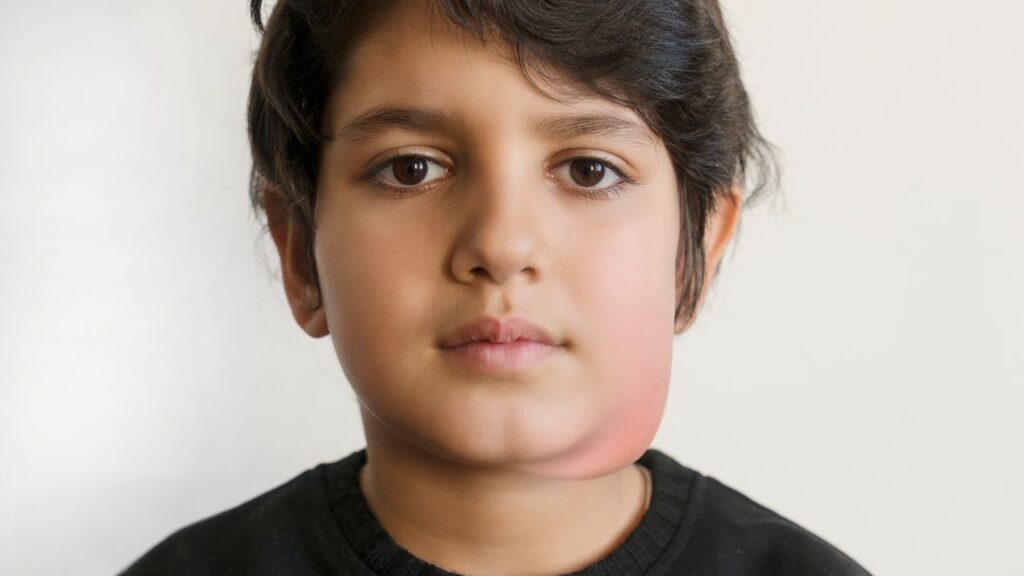
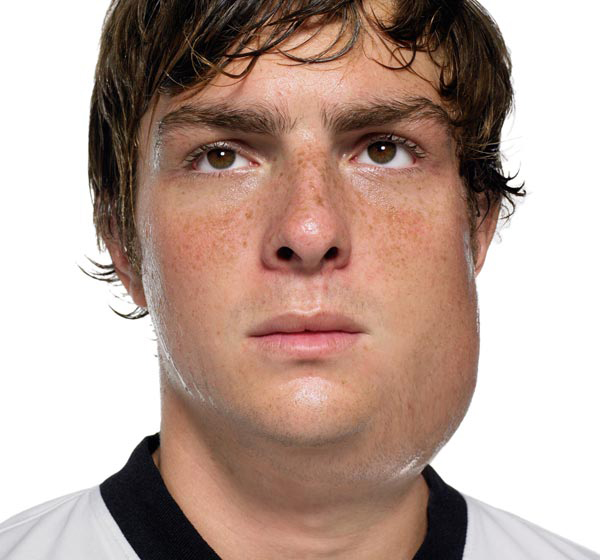
The hallmark symptom of mumps is swelling of the salivary glands, particularly the parotid glands located below the ears. This swelling leads to a characteristic “chipmunk-like” appearance. Other symptoms include fever, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, loss of appetite, and pain while chewing or swallowing.
Complications of Mumps:
While mumps typically resolves within a few weeks without complications, it can lead to severe complications in some cases. These include inflammation of the brain (encephalitis), meningitis, deafness, pancreatitis, orchitis (testicular inflammation) in males, and ovarian inflammation in females. Complications are more common in adults than in children.
Diagnosis of Mumps:
Diagnosing mumps usually involves a physical examination to assess swelling of the salivary glands. Laboratory tests, such as viral culture or polymerase chain reaction (PCR), may be conducted to confirm the presence of the mumps virus in saliva, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment of Mumps:
There is no specific antiviral treatment for mumps. Treatment primarily focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. This includes rest, adequate hydration, over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen or ibuprofen) to reduce fever and alleviate pain, and applying warm or cold packs to swollen glands for comfort.
Prevention of Mumps:
The most effective way to prevent mumps is through vaccination with the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. This vaccine provides long-term immunity against mumps and is typically administered in two doses during childhood. Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, can also help prevent the spread of the virus.
Mumps in the Context of COVID-19:

Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, concerns have arisen about the potential impact of mumps outbreaks. While COVID-19 vaccination efforts continue, maintaining high vaccination coverage for diseases like mumps remains crucial to prevent outbreaks and protect public health.
Conclusion:
Mumps, although less common today due to widespread vaccination, remains a concern, especially in areas with low vaccination rates. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for prompt diagnosis and appropriate management. Vaccination, alongside hygiene practices, remains the cornerstone of mumps prevention, highlighting the importance of public health initiatives in controlling infectious diseases.
By providing accurate information about mumps, its causes, and treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions regarding vaccination and healthcare practices, contributing to the overall well-being of communities.
Keywords:
mumps, causes, symptoms, treatment, complications, diagnosis, prevention, vaccination, MMR vaccine, contagious, viral infection, paramyxovirus, outbreaks, public health, COVID-19, hygiene practices, swelling, salivary glands.